What is Network Interface Card (NIC) - Definition, Purposes / Functions & Types
Network interface cards (NIC) are one of the most useful pieces of technology people commonly use without knowing.
You use a network interface card whenever you connect to the internet and browse the web, go on social media, or download a file.
We are going to discuss what NICs are, what they do, and how their constituents enable them to work (Purposes / Functions) . We will also cover other details, such as types of NICs and what are some devices that use them.
Let’s start with the definition of NICs.
What is NIC - Purpose and Importance

NIC stands for Network Interface Card. It is the hardware that has the necessary protocols and drivers required for networking.
Without an NIC, your device (whatever it may be) cannot connect to a network.
What is the Purpose of an NIC
The NIC is responsible for interfacing between a device and a network. It has the hardware and software required for receiving and sending signals to and from a router.
It is also responsible for converting those signals into a format that the computer/device can understand.
Importance of NIC
In the modern day, where everything relies on the internet somehow, a NIC is a necessity rather than a comfort.
You cannot connect to the internet if your device lacks an NIC. That means that you can’t do the following things.
- Work remotely.
- Take online classes.
- Use SaaS services and software.
- Update your software.
- Download software from online sources.
- Browse the web….etc.
Most of these are important things that we do daily, so that should help you understand the importance of NICs.
Which Devices Use NICs
So, what kind of devices use NICs? Well, that's quite easy. Anything that connects to the internet has an NIC. So, that means all of the following have an NIC:
- Smartphone
- Tablet
- Laptop
- Desktop PC
- Routers
- Printers
- Scanners
- Smartwatches
- IoT devices
This also brings us to our next point. A NIC can have a different size and shape depending on the device in which it is placed. Modern devices have their NICs integrated with their other hardware such that it is indistinguishable.
Desktop PCs and Laptop computers can add more NICs using either USB or PCI slots. This is typically used to add WiFi or ethernet connectivity.
Types of NIC
As we mentioned before, NICs can have different shapes and sizes. However, their major differences lie elsewhere. The common method of segregating NICs is by defining them by connection type or their max speed limit. Let’s check them out.
Connection Type
An NIC can support one of many connection types. They can be wired connections or wireless. Listed below are the details about the different types.
- Wired Ethernet. Ethernet is a wired medium for internet connectivity. Ethernet NICs have an ethernet port that accepts cat6, cat5, and other cables of the sort. They are widely used in desktop computers and laptops because of their reliability and high speeds.
- Wireless NIC. Commonly known as WiFi, wireless NICs have the hardware capable of receiving and sending WiFi signals to stay connected. There are different WiFi standards, and different NICs are made for them. For example, 802.11a WiFi standard NIC needs to be capable of receiving 2.4 GHz band signs. The 802.11ax NIC needs to be able to send and receive 2.4, 5, and 6 GHz band signals.
- USB NIC. These are small NICs that can connect to the USB port on a computer. They come in both wired and wireless forms. They are also rated for different speeds. They are typically used to add NICs to devices that don’t have integrated network cards.
Speed Type
NICs are also segregated based on their speeds. For example, two ethernet NICs may have different max speeds. There are typically brackets for speed, which are listed below.
- 10 Mbps. These are quite common and used in light local networks.
- 100 Mbps. Extremely common in commercial hardware. Suitable for light to moderate internet use.
- 1 Gbps. Typically used by medium-sized companies for running SaaS services.
- 10 Gbps. These are extremely fast NICs that are typically used in large corporations and data centers.
- >10 Gbps. Extremely rare, these NICs are exclusively used in mega data centers that require very high data transfer speeds.
These include both wired and wireless NICs. However, gigabit speeds are rarely available on wireless NICs. Ethernet is their preferred medium due to the lower costs and higher reliability.
Parts of an NIC
A network card has two major components that enable it to work. They are the driver and the MAC address.
-
Driver
The driver is software that allows a piece of hardware to communicate with the operating system of the overarching system.
In NICs, the driver is required to communicate with the Windows, MAC, Linux, or Android systems.
Without the driver, the NIC cannot pass any information to or from the operating system, thus making it useless.
Usually, when you add a NIC to a device, its drivers automatically get installed, so you don’t have to worry about it. However, drivers can get corrupted due to bad shutdowns or power failure. In this case, they must be reinstalled to restore the NIC function.
-
MAC Address
The MAC address is the most important constituent of an NIC. A MAC address is a 12-digit, hexadecimal number. This number is burned into the NIC physically. This means that it cannot be changed.
The 12 digits are further divided into two parts. The first six digits are called the OUI (Organizationally Unique Identifier), and the last six digits are the serial number of the NIC.
Here’s an example:
8F-EA-C6-E4-E2-23
In this example, the OUI number consists of the first six green numbers. It identifies the vendor or organization that created the NIC. The OUI number will be the same for all NICs created by the same organization.
The last six blue numbers comprise the serial number. They identify the individual NIC. This means that each NIC has a unique MAC address that can be used to identify it.
Why is the MAC address important in internal networking?
MAC address is important because it is used in internal networking to identify the exact device with which to communicate.
Your router and your device are part of an internal network. The router connects to the public internet and filters all the traffic. The router uses the MAC addresses of all devices on the internal network to forward the right packets to each device.
Similarly, network admins need to authorize devices to connect to their internal network using their MAC address. To do that, they first need to identify the MAC address of each device. That is typically done by opening the terminal or the command prompt and running a specific command. You can skip ahead to learn how to do that.
IT teams also need to do a MAC lookup on all internal network devices as part of their maintenance. They use the information from a MAC address lookup to troubleshoot connectivity problems with NICs and reinstall drivers.
How to Identify the MAC Address of an NIC
For network managers and admins, knowing the MAC address of all the devices connected to the network is a requirement. They can learn these addresses by doing an individual MAC address lookup on each computer.
Here’s how you can do that on different operating systems.
Windows
In Windows, you have to open the Command Prompt to find the MAC address. Just follow these steps.
- Press Windows + R to open the “Run” dialog.
- Write ‘cmd’ and hit enter.
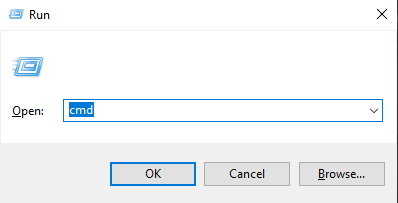
- Once the Command Prompt opens, type the following command and hit enter.
“ipconfig /all”
- A list of all your network-related information will appear. You only have to check for the following text:
Wireless LAN Adapter WiFi
Or
Ethernet Adapter Ethernet
- Under the aforementioned headings, you have to look for “Physical Address.” That is your NIC's MAC address.
MAC/Linux
MAC OS and Linux have a very similar terminal, so the same command works for both of them. Here are the steps for finding the MAC address.
- Open the terminal. In most Linux distributions, you can press Ctrl+Shift+T to open the terminal. In Mac OS, you need to go to the search menu and type terminal to find and open it.
- In the terminal, write the following command and hit enter.
“Ifconfig”
Or
“sbin/ifconfig”
- This will show you a list of network-related information. You just want to look for either:
Ether xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx random_word random_string_of_letter (Ethernet)
or
WLAN/WiFi xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx random_word random_string_of_letter (WLAN/WiFi)
- The numbers before the random_word are your NIC’s MAC address.
For other devices, you can check out this blog post to learn how to check their MAC address.
Conclusion
So, there you have it: the down low on NICs and the associated information like MAC addresses and how to find them.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Can a Device Have Multiple NICs?
Yes, if a device has an ethernet port and a WiFi antennae, then it technically has two NICs, one for the ethernet and one for the WiFi. You can also add more NICs to a computer by attaching USB NICs to it.
What Will Happen If I Have Multiple NICs?
Nothing will happen. Your computer only uses one NIC at a time, which is the one connected to the internet. Even if all of your NICs are connected, the wired connection will be favored over the others unless you disable or disconnect it.
How can you determine the manufacturer of an NIC card based on the mac address?
The first six digits of MAC address are called the OUI number. This number is assigned by the IEEE to specific companies. An OUI Lookup tool can find out which company the number was assigned to and in this way you can determine the manufacturer of the NIC.
Why Do I Need To Do a MAC Address Lookup?
Strictly speaking, you don’t. However, if you are managing a closed/private network, then you may want to know the MAC address of all devices that you want to whitelist for connection. That’s where looking up Mac addresses can be helpful.