What is a Port Number and How Can I Find it?

A port number is actually a virtual address assigned to a specific program or service running on a device. You can think of it as a smaller version of an IP (Internet Protocol) address. Note that devices on a network use IP addresses to communicate with one another.
For example, if a friend sends you a message on a social media app, let's say Messenger, that message will come with a double address. One will be the IP address of the device, and the second is the port that actually runs the messenger.
Still confused?
If so, then read on. In this article, you will find all that is necessary for you to know about what a port number is and how you can find it.
What is a Port?
Ports are the virtual endpoints in a network that protocols (e.g., TCP or UDP) use to specify different services running on a device. Each port has a unique but specified number assigned to it and is designed to perform a specific function.
Many people confuse a port address with an IP address, but they are not the same. IP addresses are device-specific, while ports are specific to the services running on a device.
The number assigned to the port varies from 0 to 65535. Some among them are reserved for specific services such as:
- Port 80 is for HTTP traffic
- Port 443 is for HTTPS traffic
- Port 53 is used for DNS traffic, and there are many more ports as well.
Not all the ports are created equal. At a time, a device only uses specific ports that are meant to provide the service related to the query. These are referred to as open ports. The rest, who are not meant to provide any service to the traffic, are considered closed ports.
Types of Ports
Ports in networking are classified into some major types based on their number ranges, protocols, and purposes. The following are some of the major types to which ports are classified.
1. Well-Known Ports (0-1023)
These ports are assigned by IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) and are reserved for core services and protocols. Such ports are used at the system level for core processes and require administrative privileges to bind on operating systems.
As an example:
- Port 20/21 is for FTP service.
- Port 22 is for the SSH service.
- Port 25 is for SMTP service.
2. Registered Ports (1024–49151)
These are also assigned by IANA and are common for proprietary services or software-specific protocols. Registered ports can be used without administrative access.
For example:
- Port 1433 for Microsoft SQL Server.
- Port 3389 for the Remote Desktop (RDP) service.
3. Dynamic or Private Ports (49152–65535)
Dynamic or private ports are also referred to as ephemeral ports. They are not assigned by IANA and are used temporarily. They are automatically allocated by the operating system (OS) when a connection request is initiated over a network.
4. TCP vs UDP Ports
Ports are also classified based on two major transport-layer protocols, namely TCP and UDP. TCP ports are considered more reliable. They are connection-oriented and are used for various services, such as web browsing and email. UDP ports, on the other hand, are less reliable and are not connection-oriented. They are used for services such as video streaming and DNS.
But, What’s the Port Number?
A port number is a digital label, or you can say an address, that is unique to all the ports on a device. The number is meant to specify the process to which a network request is forwarded when it reaches a server.
Here, we would like to address a common misconception: “My port number”.
Know that “No” such thing exists. As many of the ports on a device are represented equally, and numbers are used as presets to run the services. They do not belong to anyone.
You can only check the status of a port number using various methods. These statuses can be either:
- The port is open, indicating that an active service is running on it and it is accepting incoming traffic.
- The port is closed, which means no active service/application is running on the port, and it is not listening to traffic.
Ways to Find the Status of Port Numbers
There are several methods available to help you determine your port number status. Next, we will walk you through these methods one by one.
-
Finding Port Number on Windows
The following steps outline how to find the network port numbers on Windows.
- In the Windows search box, type “cmd” and open the “Command Prompt.”
- Type the command “netstat -a” and press “Enter”. It will list all the open ports of your device.
Remember, the values after the colon in the IP address are the port numbers. The IP address can be found in the “Foreign Address” column.
-
Getting Port Number on macOS
Follow the steps below to get the port number on macOS.
- Open the “Command Terminal” by either searching for it or pressing the “Command+Spacebar” button.
- Next, run the command “netstat -an”.
- You will receive the completed list of ports for the device, along with their corresponding numbers.
-
Finding the Port Number on iOS and Android
Finding the port number on iOS and Android was considered hard. Why? Because for this, you have to install and use external software. But that’s the old days story.
You can check the complete list of port number statuses for devices running on Android or iOS by simply providing the IP address to our online port checker tool (explained below).
How to Find the Port Number Status from IP Address?
The previously discussed methods for checking port status applied only to local devices. To find the port number status using an external IP address or a domain name, a simple method is to use an online Port Checker. Here’s how:
- Open our port checker tool.
- Once you land on our open port checker, enter the device IP address in the dedicated input box and choose the port type. You can also enter the domain name in case you want to check the ports for a website.
- After entering the IP address or domain name, select the port type you want to scan.
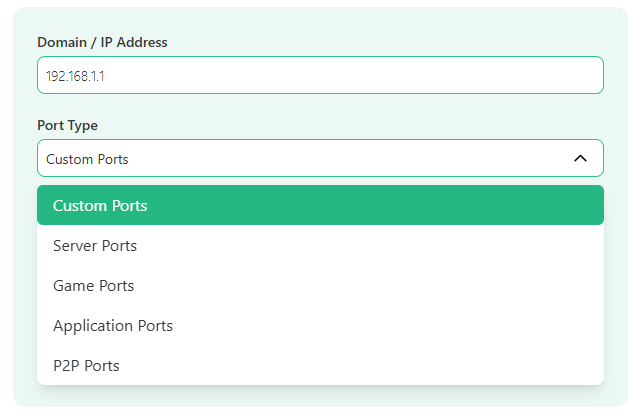
- You can also enter the custom port numbers in the “Ports” box provided at the bottom.
- After selecting the type or entering the custom port numbers, click the “Check” button at the bottom and let the tool do the job. It’s a matter of just a few seconds.
- Or, to view the list of all ports for the device, click the “Scan All Ports” option on the right.
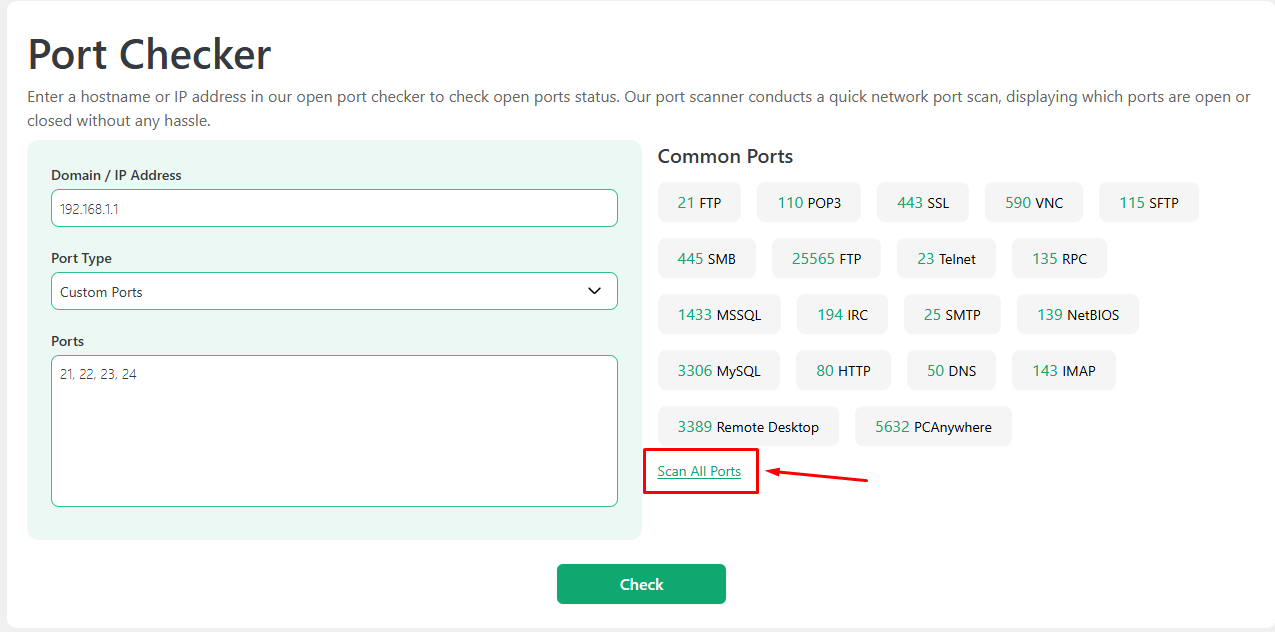
- Soon, the tool will display the complete list of ports for the provided IP address or domain name, similar to the one we have shared in the screenshot below.
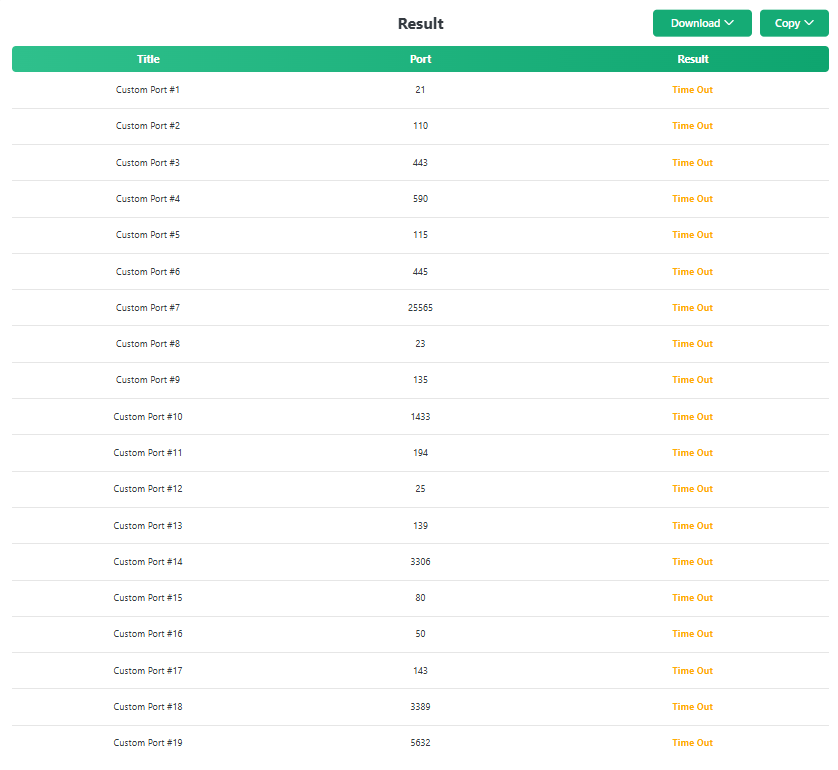
Regarding the results, the ports that show “Time Out” in the results field are closed. Ports that are being shown “Open” in the results field are the open ports that are currently running a service application.
Conclusion
Port numbers are virtual identifiers that help redirect network traffic to the specific service it is looking for. They work alongside IP addresses, allowing systems to communicate seamlessly over a network.
You can check the port number status of a device by running its IP address through our port checker tool. There are many other methods available, as we discussed in this blog post above.
Regarding why one should check the port numbers, here’s a brief for you.
Networking ports, especially those left unnecessarily, are prone to cyberattacks. Cybercriminals use them to penetrate the networks. One such common attack is a port scan attack.
To read more on this, consider checking out our blog post on what a port scan attack is and how to prevent it.