What is Port Forwarding on a Router or Network?
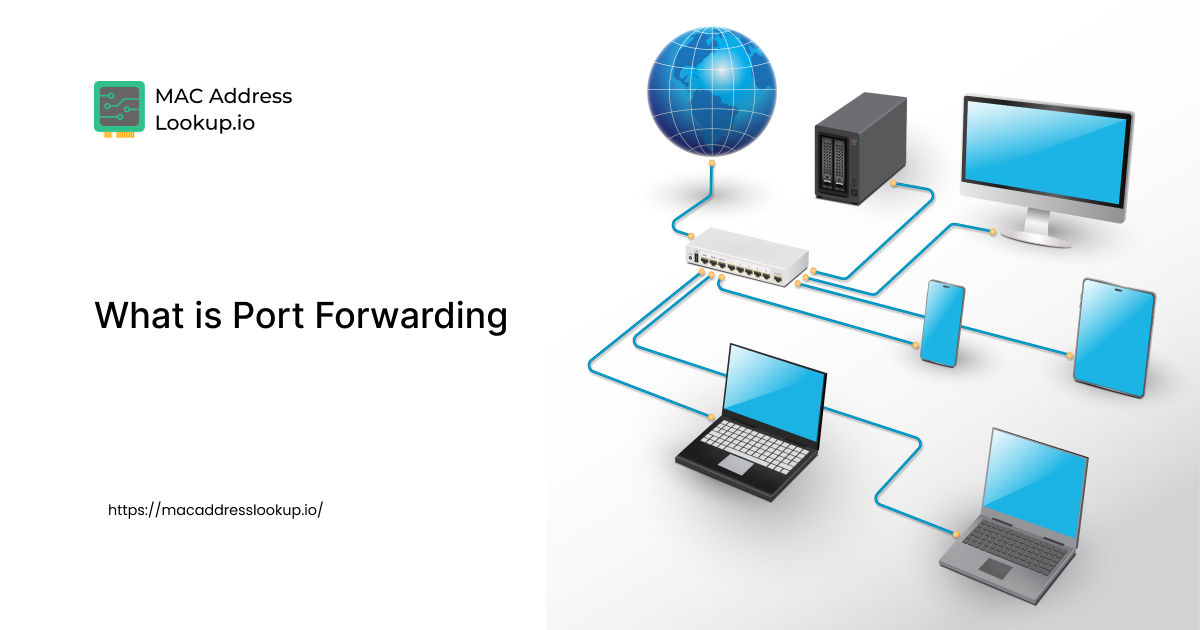
Port forwarding is a term you might have come across if you have ever hosted a game on a local server. Or you have tried to connect to a CCTV camera wirelessly. Port forwarding in a router is not a complex or advanced hacker trick. You can think of it as a basic network tweak that enables remote access to applications. In this blog post, you will learn what port forwarding is on a router and how to set it up. All explained in simple terms.
What is Port Forwarding in a Router?
Port forwarding is a technique in which you configure a router's settings to provide access to services routed on a private network to external devices. Without port forwarding being implemented, no external device can connect to the services running on a private network.
In simple terms,
If you have a service or, let's say, a game hosted on your local computer. By enabling port forwarding, you can provide access to other devices outside your network.
In port forwarding, the router is configured to send data (related to a particular service/application) directly to a specific device on a network. During this process, the router skips certain security checks and sends data instantly, resulting in faster speeds.
There are many more benefits that port forwarding provides (more on this later). However, it also comes with many risks.
For example, it acts as an entry point for cybercriminals to penetrate your network. We will also have a detailed talk on this later. However, for now, let us take you through the working of this forwarding technique.
How Port Forwarding Works on a Router?
Before we walk you through the complete process of how port forwarding works on a router, let’s clarify some basics to avoid confusion.
The network that you use at home, office, or shop is your private (local) network. At the same time, the internet is a public network. Your router device, via which you connect to the internet, acts as the gatekeeper between the two.
By default, the routers are set to block access to requests made by external devices using the internet to the services/applications you are using on your local network. This is likely done for network security purposes, so that no unauthorized access can be made.
However, when you set up a port forwarding rule for a particular service on your local network, that service becomes accessible to external devices via the internet (public network).
For your better understanding, we have explained the complete working step by step, along with a simple example, below.
Step 1. Request Made from the Public Network
Suppose you are outside and want to view the CCTV installed at home using a mobile app.
In that case, when you open the app, your mobile device will first send a request to the public IP address, targeting a specific port number. The targeted port number will be the one responsible for handling the traffic for CCTVs.
Know that at this time, the request is on the public network.
Step 2. Router Receives the Request
Your router will receive the incoming request to access the port for CCTVs from the public network. Typically, if no port forwarding rule is set up, the router will automatically deny the request.
However, if you have set up a port forwarding rule on the router for the port assigned to CCTVs, and the public network is requesting access to the same port. In that case, the router will proceed with the request further as per the rule you have decided.
As an example:
If “8080” is the port number assigned to CCTVs and you have set up the rule that whenever a request is made to the port “8080”, the router should forward it to the device having IP address “192.000.0.0”.
In that case, the router will divert the incoming traffic directly to the device with IP address “192.000.0.0”, bypassing the security checks.
Step 3. Request Forwarded to the Device
When the router diverts traffic to the dedicated device, it rewrites the request from the public IP to the private IP. This means the request has entered the public network and is being routed to your local network.
To maintain consistency in communication, routers use NAT (Network Address Translation).
Once the device receives the request, it will respond by providing access to the requested data. As per our CCTV example, it will probably be the live camera feed.
Step 4. Router Respond to the Device Making Request
The response travels back through the router to the device (in our example, your phone) over the internet. During this process, NAT will keep track of the connection and return the data to the correct external IP and port.
What is Port Forwarding Used For?
The primary purpose of the port forwarding technique is to provide access to services or applications running on your local network to the devices on the public network. Many people are using it for various purposes, such as:
- To provide users access to virtual desktops.
- To access applications while on the go, e.g., accessing CCTV cameras using a phone.
- For providing access to someone to the games or applications you are hosting locally on your personal device.
- For peer-to-peer file sharing, e.g., torrent clients.
- To access NAS (Network Attached Storage) files stored on your local network.
Types of Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is of various types. Each type is suited for use in a different scenario. Below are discussed the most common types of port forwarding being used by many at the time.
Static Port Forwarding
In static port forwarding, you set a rule in your router's settings to divert incoming traffic requesting a particular service (designated to a certain port number) to a specific device on your local network.
Dynamic Port Forwarding
This type of port forwarding is akin to a secure tunnel for your internet traffic and is often used in conjunction with SSH (Secure Shell). In dynamic port forwarding, you route to multiple destinations using multiple ports through a secure server, acting like a temporary, encrypted proxy.
This type is mostly used by networking or cybersecurity experts to browse the internet securely over untrusted networks (like public Wi-Fi).
Local Port Forwarding
It is usually used for accessing internal services (databases, intranet sites, APIs) from outside. In local port forwarding, you route the traffic from your local device (computer, laptop, etc) to the remote server hosting the service. The forwarding here is usually done while using the SSH tunnels.
Remote Port Forwarding
Remote port forwarding is usually used to expose services hosted on a local server to an external user via a remote server.
In this type, you connect to a remote server via SSH with a -R rule. A public port is opened on that remote server. When someone accesses that public port, the server forwards the traffic through your SSH connection.
That traffic reaches your local machine or private network while using the specified local port. The response travels back through the tunnel to the remote server and then to the user.
UpNp Port Forwarding
UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) port forwarding is an automatic method for apps and devices to open ports on your router.
As an example:
If you run an app that needs a public connection (e.g., a game), the app detects that UPnP is enabled on your router. If enabled, it will send a request to the router to open the port and forward it to me.
The router dynamically opens the port and maps it to the app’s internal IP. And when done, the outside world can reach your device through that port.
Unlike manual port forwarding, these rules are usually temporary and automatically closed when no longer needed.
How to Port Forward on a Router?
The process of setting up a port forwarding rule varies slightly depending on the type, make, and model of the router. Below, we have shared a general procedure that will help you implement the rule on your router.
Step 1. Log in to your router settings using its IP address (usually mentioned on the backside of the router).
Step 2. Once logged in, look for the Port Forwarding section under Settings. The name of the setting can vary depending on the router's brand. Usually, the setting is named as:
- Port Forwarding
- Virtual Server
- NAT Rules
- Firewall
Step 3. As you find the forwarding settings, you will need to fill in the following fields.
- Service Name: Any name that you want to set up, e.g., Game or Camera.
- Port Range / External Port: The port number that you want to open.
- Internal IP: IP of the device to which you want to forward the incoming traffic.
- Internal Port: The port that is used by the service or the application you want to provide access to.
- Protocol: Choose TCP, UDP, or Both
Once you have filled in the above field, restart your router. After restarting, test whether your port forwarding rule is set up correctly. A simple way to do that is to check the status of the external port you filled in the field.
For this, you can use our open port checker. Simply run the scan for the port by providing the IP address of your router. If you see “Open” next to the port number inside the results, it means the forwarding rule has been set up successfully. However, if you see “Time Out,” then there must be an error.
Port Mapping Vs Port Forwarding: What’s the Difference?
In networking, port forwarding and port mapping refer to somewhat the same thing. They have little difference in the technical context. Many people get confused and use them interchangeably. Below is a simple explanation of how they differ.
Port forwarding is the general process of allowing external devices (from the internet) to access services inside your private network. Using port forwarding, you instruct the router to forward any incoming request on a specific port of your public IP address to a particular device within your local network.
However, port mapping is a part of port forwarding. In port mapping, you define which external port maps to which internal port.
In simple terms, you can think of:
- Port mapping as the overall concept.
- Port mapping as the actual rule or action of translating one port to another.
Bottom Line
Port forwarding is a technique that involves setting up rules by configuring the router's settings. It allows you to provide external devices with access to the services or applications running on a device on your local network.
In simple terms, port forwarding allows a public network to access a service inside your local network.
Yet, the technique is beneficial but is also prone to some threats, such as increasing your network exposure to cybercriminals, who can exploit it to carry out hacking attacks. Before implementing port forwarding on a network, don’t forget to consider this crucial element.